Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics
The research conducted at IPP is concerned with investigating the physical basis of a fusion power plant, which, like the sun, is to generate energy from fusion of atomic nuclei.
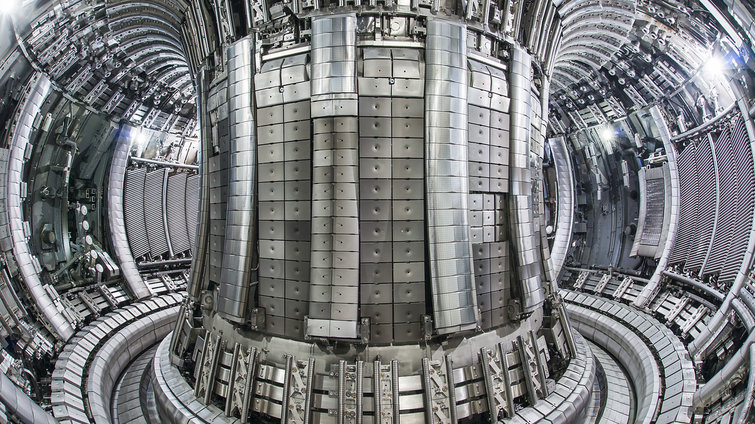
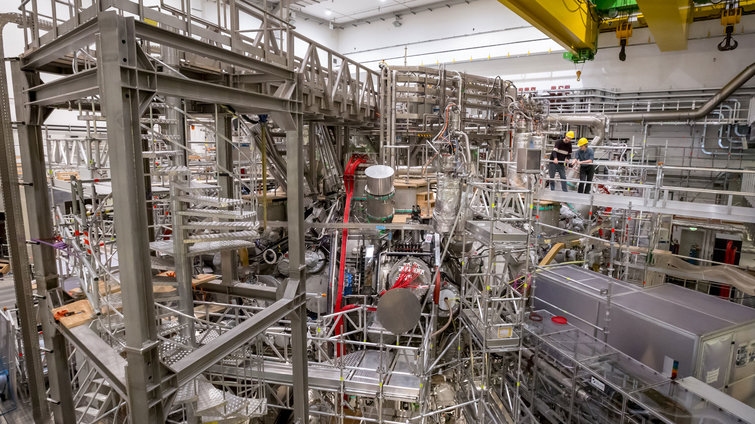
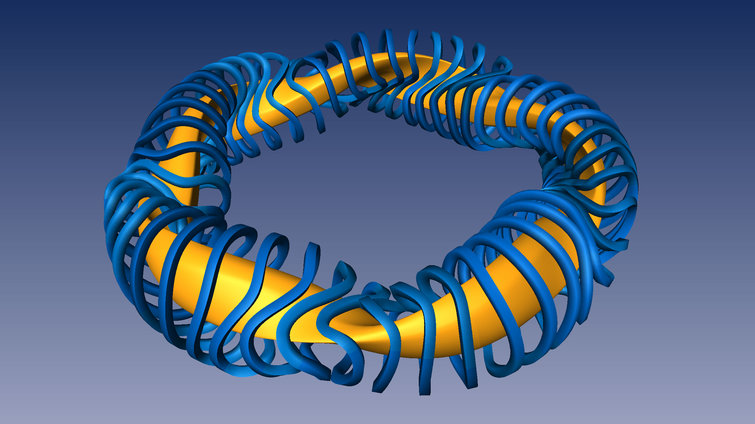
With its workforce of approx. 1,100 Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) in Garching and Greifswald is one of the largest fusion research centres in Europe: In Garching, IPP is operating the tokamak ASDEX Upgrade. The Wendelstein 7-X stellarator is being investigated at the Greifswald Branch Institute of IPP.
Ten scientific divisions in Garching and Greifswald are investigating the confinement of high-temperature hydrogen plasmas in magnetic fields, heating of plasmas, plasma diagnostics, magnetic field technology, data acquisition and processing, plasma control, plasma theory, materials research, and plasma-wall interaction.
IPP is an institute of the Max Planck Society. A long-term scientific partnership links IPP with the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centers, in particular in a joint programme on fusion research. IPP is part of the European Fusion Programme within the framework of the „European Consortium for the Development of Fusion Energy" (EUROfusion). The consortium is coordinated by IPP in Garching and comprises 30 fusion centres from 25 countries of the European Union as well as Switzerland, Ukraine and the United Kingdom. In Garching, the IPP also hosts the Programme Management Unit of EUROfusion.
The IPP's budget for 2023 totals around 146.6 million euros, shared by the Federal Government (116.3 million euros), the states of Bavaria and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (together 12.4 million euros) and - via EUROfusion - the European Union (15.6 million euros). Third parties provided 2.3 million euros.