Wendelstein 7-AS (1988 - 2002)
The Wendelstein 7-AS stellarator experiment, which was operated at IPP in Garching from 1988 till 2002, was the first test of basic elements of the stellarator optimisation. This first "Advanced Stellarator" thus paved the way for it's successor, Wendelstein 7-X in Greifswald.
The Wendelstein 7-AS stellarator experiment, which was operated at IPP in Garching from 1988 till 2002, belonged to the further developed generation of "Advanced Stellarators": Wendelstein 7-AS was distinguished from conventional stellarators by its re-computed, physically improved magnetic field generated by likewise innovative, specially shaped coils.
| Technical data: | |
| Major plasma radius | 2 metres |
| Minor plasma radius | 0,2 metre |
| Magnetic field | 2,5 - 3,5 tesla |
| Number of coils | 45 |
| Plasma volume | 1 cubic metre |
| Plasma quantity | < 1 milligram |
| Pulse length | 5 seconds |
| Plasma heating | 5,6 megawatts |
| Plasma temperature | 15 - 60 million degrees |
Objectives:
- investigation of a net-current-free plasma
- demonstration of improved equilibrium and transport behaviour due to the improved magnetic field structure
- investigation of the stability limits of the plasma
- heating of the plasma by various heating methods
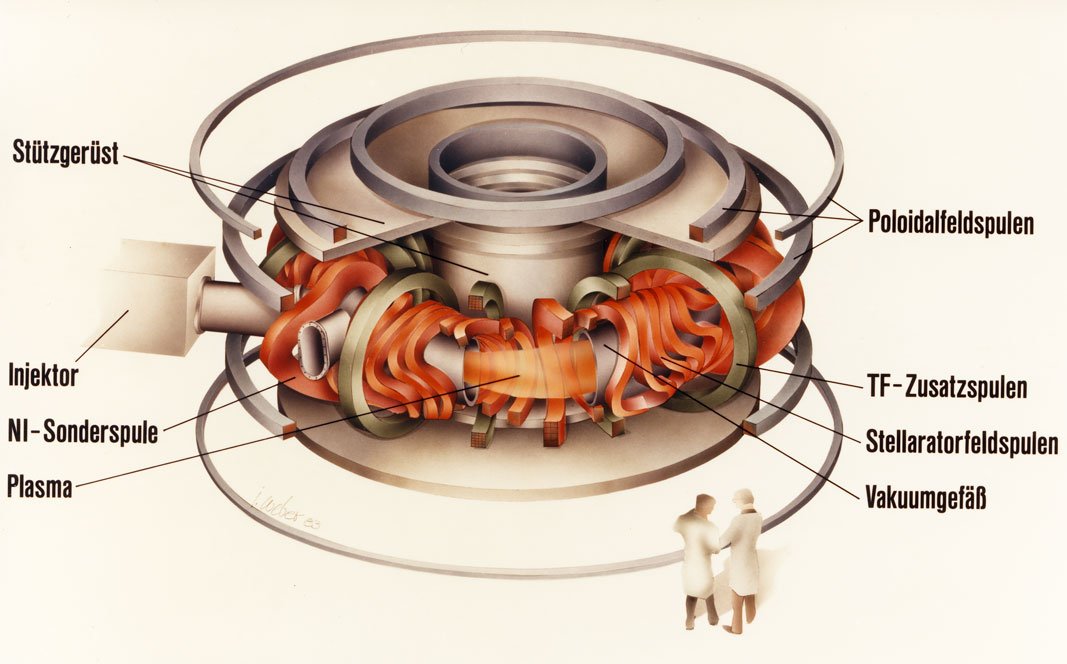
Scetch of the Wendelstein 7-AS fusion device
Graphic: IPP, I. Weber
